Understanding the Global Energy Consumption By Source
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels remain the largest source of energy consumption globally, powering everything from industrial giants to our everyday household needs. This dominance stems from their high energy density and established infrastructure, making them a convenient choice for heating, electricity, and transportation. However, the reliance on coal, oil, and natural gas is a double-edged sword, as their extraction and consumption pose significant environmental risks, driving climate change and air pollution.
Oil remains the largest single source of global energy consumption, driven mainly by transportation, petrochemicals, and industrial usage.
Natural gas is widely used for electricity generation and heating, benefiting from lower emissions compared to coal and flexible deployment.
Coal remains a significant energy source in several emerging economies, particularly for electricity generation and heavy industry, despite global decline efforts.
Other Sources
- Hydropower accounts for 16 % Hydropower remains the largest renewable energy source globally, benefiting from decades of infrastructure development.
- Wind energy reaches 9 % Wind energy has seen strong growth worldwide, supported by utility-scale installations and offshore wind projects.
- Solar contributes 5 % Solar energy is the fastest-growing renewable source, driven by declining costs and widespread rooftop adoption.
- Nuclear contributes 15 % Nuclear energy provides a stable, low-carbon source of electricity, particularly in advanced economies. While growth has been slower than renewables, nuclear remains critical for energy security and base-load power generation.
Major Energy Sources That Runs the World
- Fossil Fules: Fossil Fuels dominate with 55%
- Renewables: Renewables supply 30%
- Nuclear: Nuclear contributes 15%

Visual Intelligence by FactsFigs.com
Global Energy Insights
Data Source: ChatGPT
Overview
Global energy consumption refers to the total amount of energy utilized by individuals, industries, and nations across the planet, encompassing a diverse array of energy sources. As economies expand and urbanization accelerates, the demand for energy continues to surge, pushing us to examine not only how much energy we consume but also the foundational sources that meet this insatiable appetite. From fossil fuels to renewables, the intricate web of energy consumption brings to light the stark contrasts in energy strategies worldwide.
Delving into the nuances, we must acknowledge the staggering reliance on non-renewable energy sources like coal, oil, and natural gas, which, while efficient, raise critical environmental concerns. In contrast, the rapid rise of renewable energy sources — such as solar, wind, and hydro — offers a glimpse of a more sustainable future. However, the challenge remains: how do we transition smoothly to these greener alternatives without disrupting economic stability? By exploring cutting-edge innovations and global partnerships, we can envision a world where energy consumption is not just about quantity but quality, efficiency, and sustainability.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, are gaining prominence as the world grapples with the pressing need for sustainable energy consumption. Unlike fossil fuels, which release harmful pollutants and are finite, renewables promise a cleaner, more sustainable pathway for energy production. For instance, solar panels harness sunlight, converting it into usable electricity, while wind turbines capture kinetic energy from the wind. Not only do these energy sources reduce carbon footprints, but they also contribute to energy independence by diversifying the energy sources available to a region.
However, the transition to renewable energy is not without its challenges. High initial costs for technology installation, variability in energy supply (especially with solar and wind), and land-use concerns can complicate widespread adoption. Additionally, while renewables significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, they still require a complementary adjustment in energy infrastructure to ensure reliability. Balancing these pros and cons is key to shaping a sustainable energy future, where innovative technologies and policy frameworks can enhance efficiency and accessibility in the renewable energy landscape.
Nuclear Energy Source
Nuclear energy stands at the forefront of a debate on sustainable energy sources, offering a potent solution to the growing demands of energy consumption. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear power generates immense amounts of energy with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, presenting a clean alternative in an era of climate crisis. The efficiency of nuclear reactors means they can produce continuous, reliable power, making them crucial for stabilizing the grid as renewable sources like wind and solar become more prevalent yet intermittently available.
However, the conversation around nuclear energy often pivots on safety and waste management. Advances in technology, such as small modular reactors and improved waste recycling processes, are reshaping perceptions, making nuclear not only safer but also more adaptable. By viewing nuclear energy through the lens of innovation, we can start to appreciate its potential role in a diversified energy portfolio, one that balances the urgent need for sustainable energy consumption with the realities of our environmental responsibilities. As we seek to transition from traditional energy sources, it’s essential to consider how nuclear power can complement renewables, ensuring a stable and clean energy future for generations to come.
Conclusion
As the global landscape shifts in response to climate change and technological innovation, our approach to energy sources and consumption must evolve. The increasing reliance on renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is not just a trend but a necessity. These renewables represent a beacon of hope, offering sustainable solutions while significantly reducing our carbon footprint. Moreover, advances in energy storage technologies are empowering us to harness energy more effectively, making the transition away from fossil fuels both feasible and economically viable.
However, the disparity in energy access remains a pressing challenge. While developed nations are making strides toward sustainability, many developing regions still rely heavily on traditional energy sources, perpetuating cycles of poverty and environmental degradation. Bridging this gap through investment in clean energy infrastructure and localized solutions can pave the way for equitable energy consumption globally. As we reconsider our energy consumption habits, the imperative lies not only in adopting greener sources but also in fostering a mindset of conservation and efficiency that transcends borders, creating a collaborative effort toward a sustainable future.
Data Source and Attribution
The data presented in the visualization is derived from publicly available datasets available in blogs, internet, books, articles, research papers and / or generated with AI. Energy Sources are divided into 3 main categories : Fossil Fuels, Renewables and Nuclear.
All values are expressed in percentage of energy consumption by source of energy, may be rounded to the nearest whole number. Rankings, where shown, are derived from internal calculation methodologies and do not claim authoritative or competitive standardization.
Last Verified: Jan 2026
Other Popular Topics

The 'Vibe Coding' Revolution: How Natural Language Became the New Syntax
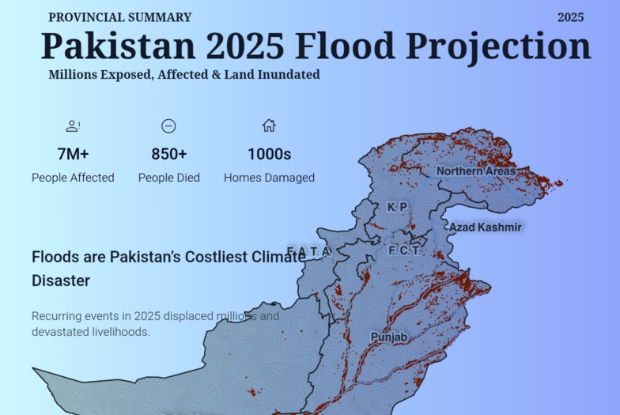
Flood Impact Across Pakistan 2025