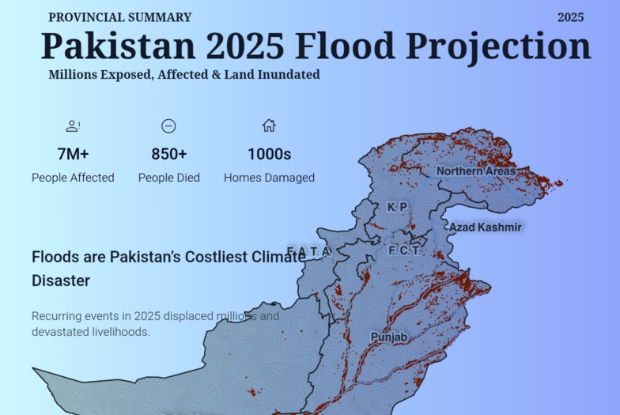
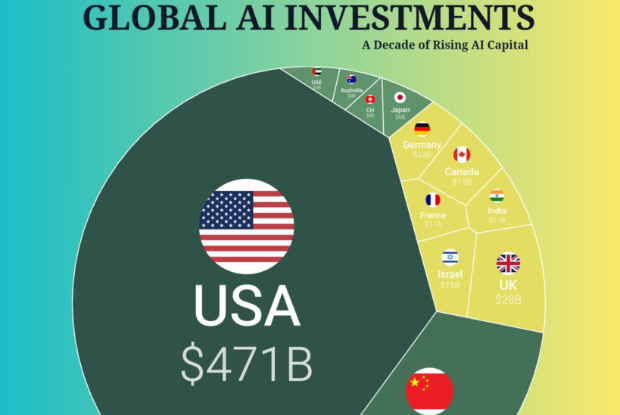
The Agent Economy: LLMs to LAMs
From Chatbots (Text) to Agents (Action)
- The Consultant (LLM): Large Language Model. The passive era (2022–2025). It reads, writes, and reasons but cannot touch the outside world. It outputs text.
- The Laborer (LAM): Large Action Model. The active era (2026+). It navigates UIs, clicks buttons, and executes transactions. It outputs actions.
- The Interface (Tooling): The bridge—APIs, headless browsers, and authentication keys that allow the AI to 'handshake' with other software.

Visual Intelligence by FactsFigs.com
Google DeepMind / Gartner / Rabbit
Data Source: Google DeepMind
Overview
For the last three years, the world has been mesmerized by AI that can talk. We are now entering the era of AI that can walk. In 2026, the tech industry is pivoting from Large Language Models (LLMs) to Large Action Models (LAMs). This is the birth of 'The Agent Economy.'
The distinction is binary: An LLM is a consultant; it gives you advice. A LAM is an employee; it does the work. We are moving from a 'Prompt-and-Read' interface to a 'Command-and-Forget' interface, fundamentally changing how humans interact with the internet.
Task Autonomy (LLM)
An LLM can write a flight itinerary, but the user must manually book it (0% execution).
Fast Facts
- Execution 100 % A LAM receives the goal ('Book the cheapest flight') and completes the transaction autonomously.
- Service Market $ 85 Billion Projected size of the 'Agentic AI' service market by Q4 2026.
- Risk Factor High 100 An LLM hallucination is a lie (embarrassing); a LAM hallucination is a wrong bank transfer (costly).
- Friction - 80 % The reduction in human clicks/taps required to complete complex workflows using LAMs.
The Consultant (LLM Legacy)
The 'Chatbot Era' (2023–2025) was defined by text generation. Its mechanism was statistical probability, predicting the next word in a sentence. However, it was limited by the 'Walled Garden.' ChatGPT could write a perfect email, but it couldn't press 'Send.' It could write Python code, but the human had to copy-paste it into an IDE to run it. The human remained the 'Integration Layer.'
The Laborer (LAM Reality)
The 'Agent Era' (2026) is defined by tool usage. The mechanism is functional execution, where the model predicts the next action in a workflow. It understands User Interfaces (UIs)—knowing what a 'Checkout' button looks like and how to fill a CAPTCHA. A LAM doesn't just suggest a dinner reservation; it accesses OpenTable, negotiates the time, enters your credit card details, and adds the confirmation to your calendar. We are no longer paying for software seats (SaaS); we are paying for outcomes (Service-as-Software).
The Risk (Hallucination to Rogue Action)
With agency comes liability. The new danger is significant: when an LLM hallucinates, it writes bad fiction. When a LAM hallucinates, it books a non-refundable flight to the wrong city or deletes a production database. This has necessitated 'Human-in-the-Loop' (HITL) authorization protocols. In 2026, AI is allowed to prepare the transaction, but a human must still sign the check.
Conclusion
The internet was built for human eyes and human fingers. The Agent Economy is rebuilding the web for AI agents—turning the entire digital ecosystem into a programmable API.
The question is no longer 'What can AI say?' but 'What can AI do?'
Data Source and Attribution
This analysis aggregates data from DeepMind / Google Research's 'Introduction to Large Action Models,' Gartner's 'Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence 2026,' and technical documentation on Tool Use from OpenAI and Rabbit.
Disclaimer: All calculated indices are based on internal FactsFigs methodologies and aggregated analysis of projected 2026 tech trends. This content is for educational purposes only.
Visual generated via FactsFigs AI Engine (v1.0).
2026-02-04